RF (radio frequency) filters are essential components for ensuring reliable and high-performance communications. They allow specific frequency bands to be selected or rejected, thereby optimizing signal quality and effectively reducing interference.
Indispensable across many fields, RF filters are used in wireless communication systems, cellular networks, as well as measurement and test equipment. Their key role in processing and managing radio-frequency signals makes them a critical element for any application requiring precision, stability, and performance.
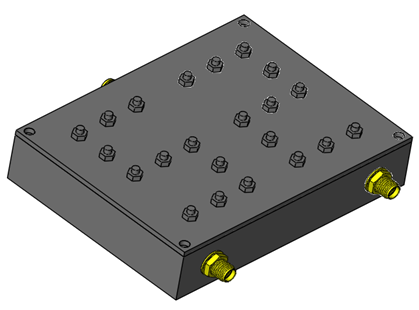
Allow precise filtering of useful bands while eliminating unwanted parasitic signals.
Available in low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop versions.
Improve the signal-to-noise ratio and ensure better RF communication reception.
Can be integrated into telecommunication systems, cellular networks, test equipment, and embedded solutions.
Consistent frequency behavior ensures long-term reliability and accuracy.
Cavity-based or lumped-component (L, C) filtering.
High-quality materials ensure resistance to demanding environmental conditions.
Ideal for applications requiring rigorous RF spectrum management and high transmission accuracy.
This type of filter allows frequencies below a certain cutoff value to pass through and attenuates frequencies above that value. It is commonly used to eliminate high-frequency noise in audio and video signals.
Unlike a low-pass filter, a high-pass filter allows frequencies above a cutoff value to pass through and attenuates frequencies below that value. It is often used to eliminate low-frequency noise and interference in communication systems.

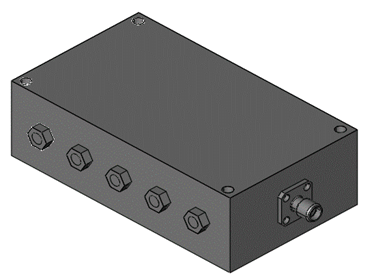
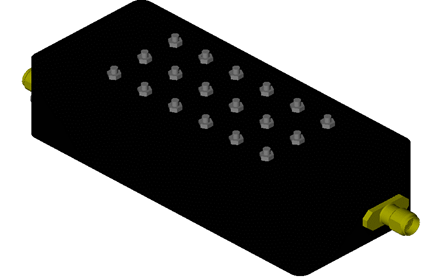
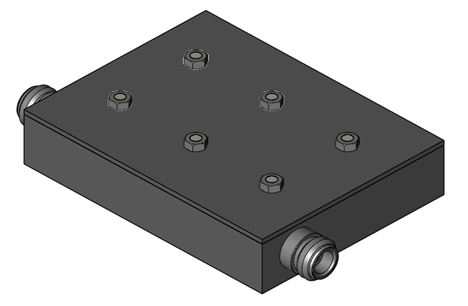

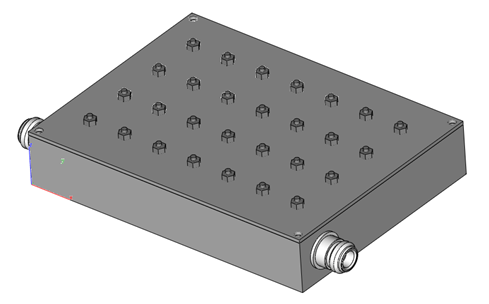
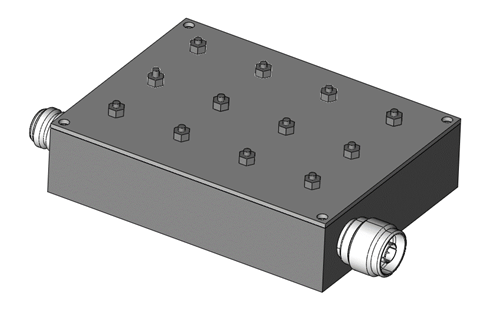
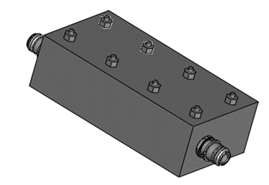

This filter allows a specific frequency band to pass through and attenuates frequencies outside this band. It is used in communication applications to select a particular frequency range, such as in radio receivers.
Also known as a band-stop filter, this type of filter attenuates a specific frequency band while allowing frequencies outside that band to pass through. It is used to eliminate interference at a particular frequency, such as unwanted signals in communication systems.
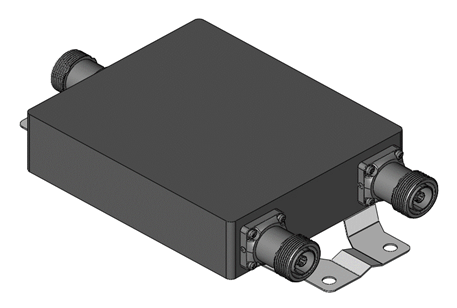
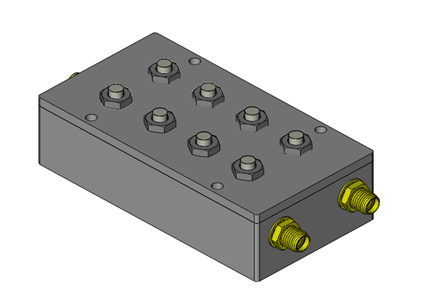
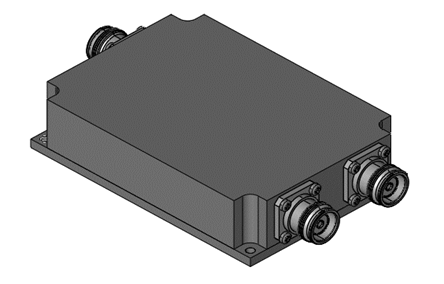

A diplexer is a device that combines or separates two distinct frequency bands. It is commonly used in communication systems to enable a single antenna to transmit and receive signals on different frequency bands.
Similar to a diplexer, a triplexer allows three separate frequency bands to be combined or separated. It is used in communication systems to manage multiple frequency bands with a single antenna.
This type of filter allows frequencies below a certain cutoff value to pass through and attenuates frequencies above that value. It is commonly used to eliminate high-frequency noise in audio and video signals.
Unlike a low-pass filter, a high-pass filter allows frequencies above a cutoff value to pass through and attenuates frequencies below that value. It is often used to eliminate low-frequency noise and interference in communication systems.










This filter allows a specific frequency band to pass through and attenuates frequencies outside this band. It is used in communication applications to select a particular frequency range, such as in radio receivers.
Also known as a band-stop filter, this type of filter attenuates a specific frequency band while allowing frequencies outside that band to pass through. It is used to eliminate interference at a particular frequency, such as unwanted signals in communication systems.








A diplexer is a device that combines or separates two distinct frequency bands. It is commonly used in communication systems to enable a single antenna to transmit and receive signals on different frequency bands.
Similar to a diplexer, a triplexer allows three separate frequency bands to be combined or separated. It is used in communication systems to manage multiple frequency bands with a single antenna.
